What Are The Most Common Treatment Options For Lung Cancer?
Every year, lung cancer claims more lives than breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers combined, highlighting the urgent need for effective treatment options. Surgical interventions, when feasible, remain one of the first lines of defense, particularly for early-stage lung cancer. Radiation and chemotherapy have also played prominent roles, often working side by side with more modern approaches.
The introduction of targeted therapies and immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment landscape, providing hope for patients with advanced stages. Targeted therapy focuses on specific genetic mutations of cancer cells, while immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Such advancements not only reflect decades of dedicated research but also embody personalized approaches to medicine, offering tailored solutions to patients worldwide.
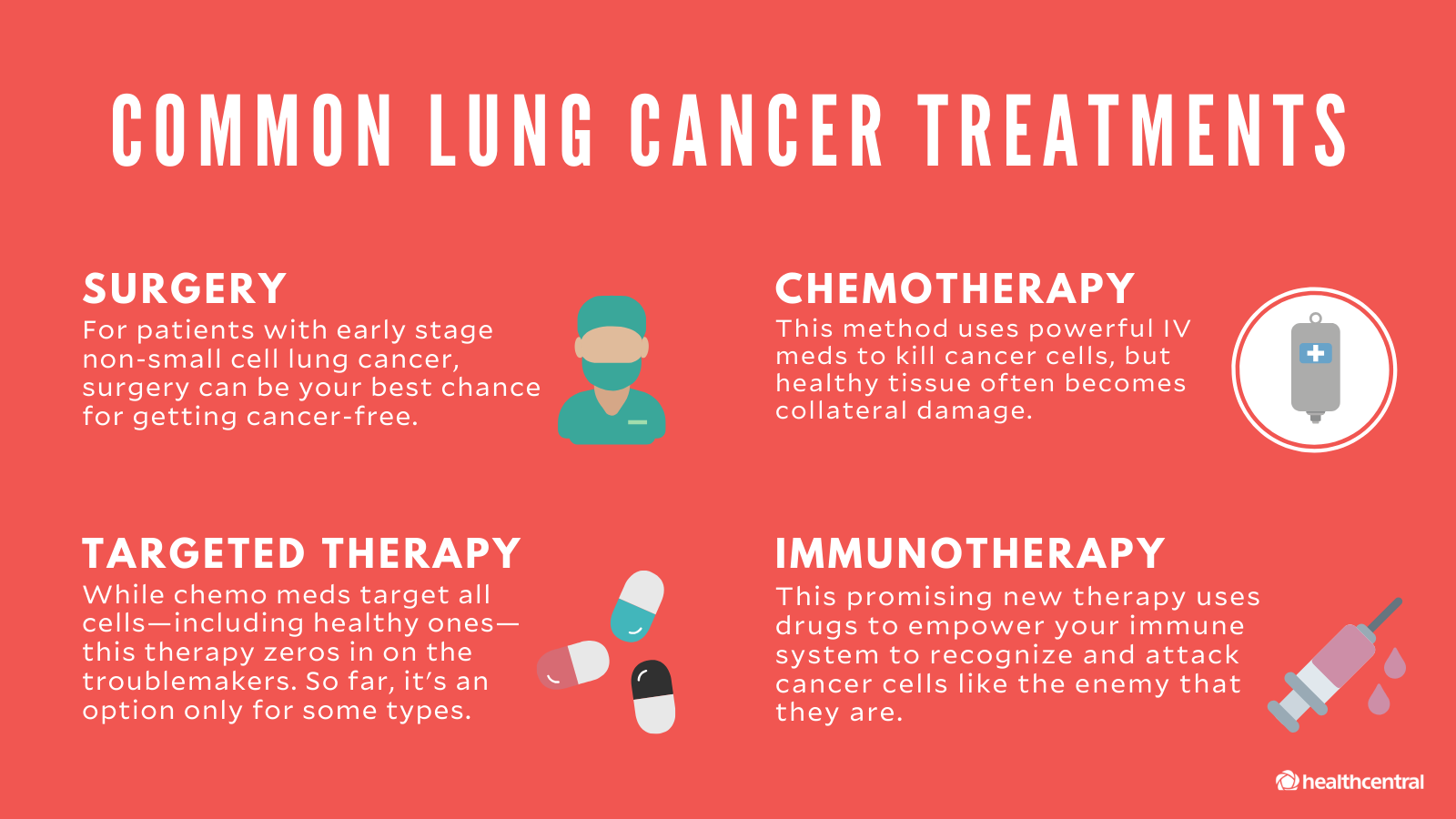
Most common treatment options for lung cancer
Surgery is often one of the first treatment options for lung cancer, especially if the cancer is detected early. Doctors may remove part or all of the affected lung, depending on how far the cancer has spread. This can be a significant procedure, but it offers a chance for a cure. After surgery, some patients may need further treatment to ensure all cancer cells are removed. Recovery from surgery takes time, but it is a crucial step for many.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are also common treatments for lung cancer. These methods are often used to target cancer cells that remain after surgery or if the tumor is too large to remove entirely. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy involves medication that travels through the bloodstream to kill any lingering cells. Both treatments can have side effects, so doctors work closely with patients to manage them.
Targeted therapies are a newer approach, providing hope to those with certain types of lung cancer. These treatments focus on specific genes or proteins found in cancer cells. By targeting these areas, they can stop cancer from growing or spreading without affecting healthy cells. This method can sometimes be more manageable than traditional chemotherapy. Thanks to advances in research, treatments are becoming more personalized and effective.
Immunotherapy is another exciting option in lung cancer treatment, helping to boost the body’s natural defenses. This therapy uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function. It can teach the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. While not suitable for everyone, it has shown promising results in some patients. Ongoing research aims to make this option available to more people in need.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical intervention is often a major option for treating lung cancer. When the cancer is in its early stages, surgery can effectively remove the tumor. Doctors usually recommend this type of treatment when the cancer hasn’t spread. In some cases, only a section of the lung, called a lobectomy, is removed. Other times, the entire lung may need to be taken out.
There are different types of surgical procedures depending on the patient’s condition. These procedures include lobectomy, pneumonectomy, and wedge resection.
- Lobectomy: Removes one of the lobes of the lung.
- Pneumonectomy: Involves removal of an entire lung.
- Wedge Resection: Excises a small, wedge-shaped piece of the lung.
Each type of surgery has its own risks and benefits.
Patients considering surgery must be evaluated to see if they are good candidates. Doctors will perform various tests to check the health of the lungs and the heart. It is important because these tests help minimize complications. People with other health issues may not be suitable for surgery. In such cases, alternative treatments might be explored.
Recovery after lung surgery can take time and requires proper care. Patients may experience pain and require assistance with breathing exercises. These exercises help restore lung function and prevent complications. It’s crucial for patients to follow post-operative instructions carefully. With time, most patients can return to normal activities.
Role of Radiation and Chemotherapy in lung cancer treatment
Radiation therapy plays a significant role in treating lung cancer. It uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. This treatment is especially helpful when surgery isn’t an option. Radiation can also shrink tumors before surgery or relieve pain. It’s often used in combination with other treatments to improve outcomes.
Chemotherapy is another crucial method in battling lung cancer. It involves taking drugs that kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. These drugs can be administered orally or through an injection.
| Treatment Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Neoadjuvant | Reduce tumor size before surgery |
| Adjuvant | Eliminate remaining cells post-surgery |
| Palliative | Reduce symptoms in advanced stages |
Each type of chemotherapy serves a distinct purpose depending on the cancer stage.
Combining radiation and chemotherapy can be highly effective for certain lung cancer cases. This combination is known as chemoradiotherapy. It amplifies the impact on cancer cells, making them more vulnerable. Patients who undergo both treatments often have better survival rates. However, they should be aware of the increased side effects.
Managing side effects is essential during and after treatment. Some common side effects include fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. Healthcare providers offer support and guidance to ease these discomforts. Patients are encouraged to maintain good nutrition and rest. Taking care during treatment can make recovery smoother.
Revolutionizing treatment with Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies have changed how we treat lung cancer by focusing on the unique features of cancer cells. Unlike traditional treatments, they attack specific genes or proteins involved in cancer growth. This precision helps preserve healthy cells, reducing side effects. For many patients, these treatments offer hope where others might not work. Research continues to find new targets, expanding options for personalized medicine.
Some lung cancers carry mutations that can be targeted effectively. Drugs such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors work by blocking signals that tell cancer cells to grow. Patients with certain genetic changes like EGFR or ALK mutations might benefit from these drugs. Testing for these mutations is an important step before starting treatment. Knowing the genetic makeup of the cancer can lead to better outcomes.
Targeted therapies are often used in combination with other treatments. For instance, they can be paired with chemotherapy or radiation to enhance results. This approach can be more effective than using one treatment alone. While effective, these therapies can still produce side effects. Doctors monitor patients closely to adjust treatments as needed.
Timing and sequencing are crucial for targeted therapy. Sometimes, they are given as first-line therapy if mutations are present. Other times, they are used after standard treatments fail. Understanding when to start and stop therapy is essential for its success. Physicians rely on a variety of tests to make these decisions.
The cost of targeted therapies can be high, but they often offer better quality of life. Insurance may cover part of the expenses, and assistance programs are available. Access to these treatments is improving, giving many more people a chance to benefit. As researchers make progress, these therapies are likely to become even more accessible. They represent a promising direction in cancer care.
Continuous learning and adaptation are key to maximizing the potential of targeted therapies. Education for patients and healthcare providers is important to keep up with advances. Workshops and seminars help spread knowledge about these innovative options. Empowered with information, patients can make more informed choices. Collaboration between doctors and patients leads to the best outcomes.
Importance of Immunotherapy in tackling lung cancer
Immunotherapy is a groundbreaking treatment in the fight against lung cancer, as it harnesses the body’s immune system. This treatment encourages the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. It has introduced new hope for patients, especially those who don’t respond to traditional therapies. Immunotherapy can be more effective and less toxic than some other cancer treatments. Its benefits have revolutionized cancer care by offering durable responses.
Several types of immunotherapy are used in lung cancer treatments.
- Checkpoint inhibitors: These drugs help the immune system recognize cancer cells as threats.
- Cancer vaccines: They boost the immune response to cancer-specific antigens.
- T-cell transfer therapy: Involves modifying a patient’s T-cells to better attack cancer cells.
Each type targets the immune system differently but aims for the same goal: enhancing immune response against cancer.
Combining immunotherapy with other treatments can improve outcomes in lung cancer care. When used with radiation or chemotherapy, it can enhance the immune response. This strategy often yields better results than any single treatment alone. Patients’ responses vary, so doctors tailor treatments to individual needs. Such personalized approaches increase the chances of success and improve quality of life.
Managing side effects is integral to the patient’s journey with immunotherapy. While generally more tolerable, these treatments can still cause fatigue and skin reactions. Doctors monitor patients closely to address any issues swiftly. Supportive care helps to tackle any discomfort caused by treatment. Through ongoing care, patients can lead healthier lives during therapy.
Research and development are key to expanding the use of immunotherapy in lung cancer. Scientists work tirelessly to discover new ways the immune system can combat cancer. Clinical trials continue to test and refine these treatments. As breakthroughs emerge, more lung cancer patients may benefit. The future of immunotherapy promises broader applications and hope for many.
Personalized Medicine: Tailored solutions for lung cancer patients
Personalized medicine is transforming lung cancer treatment by customizing approaches for individual patients. It involves analyzing the genetic makeup of someone’s cancer to determine the best treatment plan. This helps doctors target specific variations in cancer cells, improving the chances of success. As a result, treatments become more effective and tailored to each person’s unique needs. Such precision techniques are changing the cancer treatment landscape.
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in developing a personalized treatment plan. By identifying mutations and genetic variations in tumors, doctors can choose therapies that directly target cancer cells.
| Mutation Type | Targeted Therapy |
|---|---|
| EGFR Mutation | EGFR Inhibitors |
| ALK Rearrangement | ALK Inhibitors |
| ROS1 Rearrangement | ROS1 Inhibitors |
This approach ensures that therapies are more effective and side effects are minimized.
Collaboration between doctors, researchers, and patients is vital for the success of personalized medicine. Healthcare teams work together to devise the most suitable treatment plan. Patients are encouraged to ask questions and be actively involved in their care. This teamwork fosters confidence and empowers patients in their fight against cancer. Open communication ensures everyone is on the same page.
Personalized medicine also considers factors beyond genetics, such as lifestyle and environment. Doctors examine all aspects of a patient’s life to create a comprehensive treatment strategy. These insights help tailor prevention and intervention plans. By focusing on the whole person, healthcare professionals aim to optimize treatment success. This holistic approach is a significant advancement in patient care.
Despite its potential, personalized medicine faces certain challenges, including cost and access to testing. While these barriers exist, insurance coverage and assistance programs can help. Advances in technology and research continue to pave the way for more accessible solutions. The goal is to make personalized medicine a reality for every lung cancer patient. As this field grows, more people are likely to benefit from these innovative approaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lung cancer is a serious health issue affecting many people worldwide. Understanding treatment options and the innovation in medical advances can offer valuable insights for patients and their families.
1. How does targeted therapy work in lung cancer treatment?
Targeted therapy works by focusing on specific genes or proteins responsible for cancer growth. These therapies attack only the cancer cells, sparing healthy ones, which reduces side effects. They are particularly effective for patients with specific genetic mutations, such as EGFR or ALK mutations. This precision approach ensures that treatment is more effective and specifically tailored.
Doctors often conduct genetic tests to determine if a patient is eligible for targeted therapy. These therapies can be delivered as pills or injected substances, depending on the type and stage of cancer. Patients generally experience fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy, making targeted therapy a promising option for many.
2. What role does immunotherapy play in lung cancer treatment?
Immunotherapy is a cancer treatment that utilizes the patient’s immune system to fight cancer. It enhances the immune system’s natural ability to detect and destroy cancer cells. For lung cancer patients, immunotherapy offers hope by improving survival rates and reducing tumor growth. It’s especially beneficial for those who don’t respond to conventional methods.
Patients receiving immunotherapy might experience fewer side effects compared to other treatments. This is because it specifically targets the immune response, reducing harm to healthy cells. Ongoing research aims to make immunotherapy accessible to more patients, continually improving outcomes in lung cancer treatment.
3. Are there side effects associated with lung cancer surgery?
Lung cancer surgery, like any major procedure, comes with potential side effects. Common issues include pain, infection risk, and changes in lung function. However, skilled surgical teams work diligently to minimize these risks. Patients are carefully monitored and receive prompt treatment for any complications that arise.
Recovery time varies, but many patients experience improvement over weeks to months. Supportive care and rehabilitation exercises are vital during the recovery process. These steps help in regaining strength and adapting to changes in lung function, ultimately enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
4. How is chemotherapy administered in lung cancer treatment?
Chemotherapy for lung cancer is administered in cycles, with breaks in between to allow the body to recover. It can be given intravenously or orally, depending on the drugs used. The goal is to destroy cancer cells, which might have spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Patients may experience side effects like fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. Healthcare providers offer supportive care to manage these effects. Chemotherapy proves crucial for shrinking tumors and controlling cancer’s spread, offering a vital tool in the lung cancer treatment arsenal.
5. Can lifestyle changes impact lung cancer treatment outcomes?
While lifestyle changes cannot cure lung cancer, they can significantly support treatment. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking can improve overall well-being and enhance treatment effectiveness. Patients who adopt such changes often report better energy levels and reduced treatment side effects.
Support networks play a crucial role, offering encouragement and practical help. Mental health support, such as counseling, can assist in coping with the emotional challenges. Together, these lifestyle adjustments contribute to a more comprehensive and effective approach to managing lung cancer.
Conclusion
The treatment landscape for lung cancer is constantly evolving, offering hope to patients through various advanced options. From the precision of targeted therapies to the personalized approach of individualized medicine, each method plays a significant role. These innovations, coupled with traditional methods like surgery and chemotherapy, provide a comprehensive approach to care.
Collaboration between healthcare providers, researchers, and patients remains key to further advancements. As technology and research progress, more personalized and effective treatments will become accessible. With continued efforts, the future of lung cancer treatment looks promising, aiming for better outcomes and improved quality of life for patients worldwide.